What Is RFID?
RFID is an abbreviation for radio-frequency identification, a wireless, non-contact transfer of data using radio-frequency waves. Radio-frequency identification has come a long way since its original use in World War II.
Back then, military bases used it to determine whether aeroplanes were friendly or foe. Not only is the technology improving year after year, but the costs of implementing and operating an RFID system are also reducing. Making RFID more cost-effective and efficient.

KEY TAKEAWAYS
- RFID is a wireless, contactless transmission of data using radio frequency waves. It consists of two parts: tags and readers.
- The tags can be used in inventory management, personal tracking, ID badging and supply chain management.
- Radio-frequency identification technology uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to your items.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



RFID Components
RFID systems are composed of two parts: tags and readers. These tags have become an essential element of everyday life, and their use is growing.
Consider the label on a product at the store or the little device/sticker on a window screen that allows fine-free toll road use. They’re both RFID tags. The tags work with a reader. A device with single or multiple antennas that send out radio waves and receive signals from RFID tags.
What Is Radio-Frequency Identification Used for?
RFID is a versatile technology. The technology is used widely in several industries; for example, in supply chains, you can use it to track parts and accessories as they transform into finished products. In a library, it can be useful in keeping track of items checked out of the library. RFID finds use in many more commercial and industrial settings. For example:
- To track pets and livestock
- In cargo and supply chain logistics
- In vehicle tracking
- For security and access control
Importance of Radio-Frequency Identification
What advantages can RFID provide to your company? What problems can RFID solve? Read on to see how RFID technology might help you solve some typical difficulties in your business.
In the retail industry, theft is a prevalent problem that leads to inventory inaccuracies and income loss. RFID tagging of merchandise, as well as readers at entry/exit points and customer restrooms, can help you prevent theft in your business.
It’s aggravating when shelves of high-selling products are empty, and no resupply is in sight. This can result in lost sales, even while your inventory system indicates that products are available. By integrating RFID with your inventory system, you can rapidly resolve out-of-stock concerns.
An RFID system will determine whether the stock is in the backside of the shop and fast-correct inventory for automated restocks. Therefore, ensuring that you always have a consistent supply of best-selling products in your store.
When it comes to overstock, radio-frequency technology can provide accurate, real-time inventory visibility. So that multiple chain stores can decide whether to shift overstocks to other stores (that are short of stock) rather than listing the products for markdown.
What Is a RFID Application
RFID tags are becoming so common in our society that the average shopper comes into contact with RFID tags daily without realizing it. Below are some of the common ways you can apply these tags:
Inventory Management
Stock control and inventory management have been revolutionized thanks to RFID technology. Using this technology for stock management is quick and straightforward, improving your business’s accuracy, stock reliability, sales, and customer happiness. RFID stock management also provides real-time and detailed inventory information. Furthermore, it offers detailed information on your stock (quantity, models, colour, size). RFID tags can minimize stocking issues and boost security in your retail store because all items are tracked.
Simultaneous scanning of products using an RFID reader reduces the time spent on inventories, resulting in increased production and reduced manual labour for your employees. Instead of stock-taking, your employees may focus on sales and customer service with RFID technology.
Personal Tracking
Have you ever had difficulty locating a lost pet? An RFID tag can help you find your pet the next time it goes missing. It is also useful in tracking personal belongings, items, and even cars.
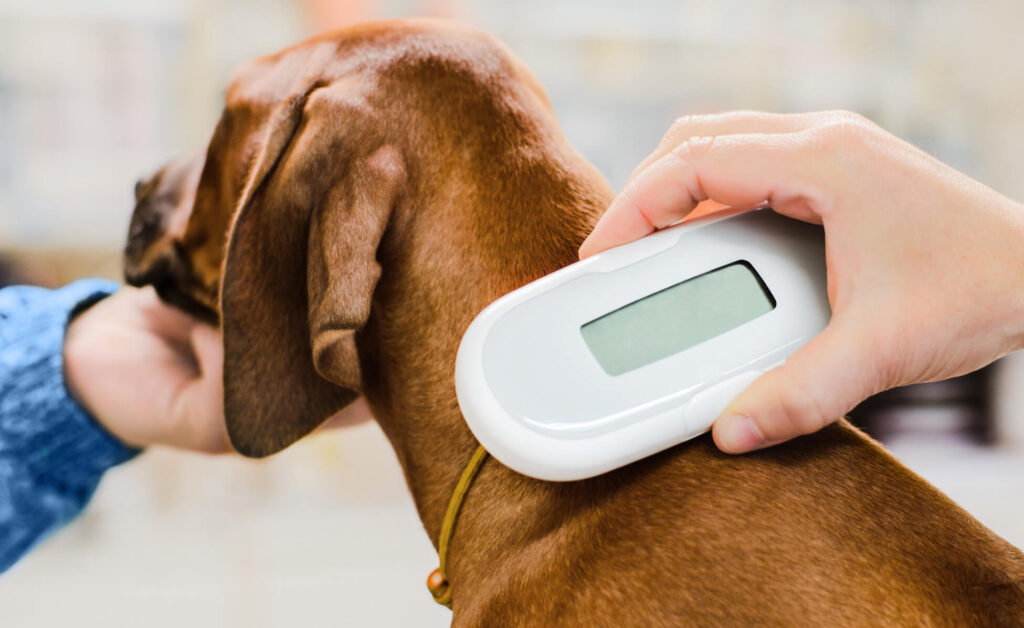

ID Badging
Not only can RFID tags be used to identify and track objects. You can also use them to identify and track individuals. For this purpose, you would use an ID badge card made of durable PVC that works with standard UHF Gen 2 systems. You can use it to identify employees, contractors, vendors, or others in government buildings, military facilities, hospitals, banks, credit card firms, insurance companies, and any other business or organization that handles sensitive data or large sums of money. When it comes to picking ID cards for students and school personnel, RFID cards may be a good option.
Supply Chain Management
Radio-frequency identification holds a lot of potential in the supply chain. It addresses some of the most pressing issues in supply chain management, for example it will:
- Assist you in maintaining minimal labour costs.
- Help you collect, manage, and analyse enormous amounts of data.
- And most importantly, it will help you in defending against security threats.
How Does RFID Work?
Radio-frequency identification is a technology that employs electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to your items. A radio transponder, receiver, and transmitter make up an RFID system. The tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader when triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby reader device. You can use this number to keep track of your inventory.
The RFID reader’s probing radio waves provide energy for passive tags. It can read active tags powered by a battery from a larger distance, up to hundreds of meters.
What Is an RFID Chip?
Radio-frequency identification chips are small computer chips connected to miniature antennas placed on or in your items. Toll booths, transit cards, passports, and contactless entrance keys are just a few of the applications where “contactless” authentication is desired.
What Are Smart Labels?
Smart Label, also known as Smart Tag, is a transponder with an exceptionally flat configuration sitting beneath a traditional print-coded label. The label incorporates a chip, antenna, and bonding wires as an inlay. Labels, composed of paper, cloth, or plastic, are created as a paper roll with the inlays laminated between the rolled carrier and the label media for use in special printer machines.
Security Risks of RFID
Radio-frequency identification systems are vulnerable to physical and electronic attacks, like other devices and networks. Hackers that want to steal private information, get access to secure areas, or bring a system down for personal benefit are becoming more common as technology advances and becomes more widespread. The following are five known security attacks that hackers can use against an RFID system.
Security Attacks Hackers Can Use Against RFID Systems
RFID tags and readers, like other items, can be reverse-engineered; however, success would necessitate a thorough understanding of the protocols and features of your RFID. To acquire data from the IC, hackers would disassemble your chip to figure out how it functions.
A hacker only needs a cell phone to perform power analysis in your RFID. Hackers can launch power analysis attacks on radio-frequency identification systems by monitoring the power consumption levels of your RFID tags. Researchers discovered this hacking approach when investigating the power emission levels of smart cards, particularly regarding the difference in power levels between a correct passcode and an incorrect passcode.
Eavesdropping occurs when an unauthorized radio-frequency identification reader listens in on conversations between your tag and reader and subsequently acquires critical information. The hacker must still understand the precise protocols, tags, and RFID reader information for this strategy to work. Replay attacks are based on eavesdropping and occur when one section of a radio-frequency identification system’s transmission is recorded and then ‘replayed’ to the receiving device later to steal information or acquire access.
During the transmission of a signal, a man-in-the-middle attack may happen. The hacker listens for communication between a tag and reader, similar to eavesdropping, and then intercepts and manipulates your data. The hacker intercepts the original signal and then provides fake data while impersonating a normal RFID component.
A Denial of Service attack refers to any failure of your radio-frequency identification system that is linked to an attack. Physical attacks are common, such as using noise interference to jam the system, blocking radio signals, or even removing or disabling RFID tags.

Benefits of RFID Technology
Radio-frequency identification systems are useful to large and small organizations because they automate operations and increase asset utilization and quality, improving productivity and cutting costs.
Here are the four major benefits:
- Most businesses struggle to keep track of assets and materials, whether it’s components on a production line, finished products being shipped, industrial containers that need to be returned, or tools, laptops, and other high-value equipment that frequently go missing. Radio-frequency identification devices provide a quick and reliable way to track them without counting each item.
- RFID applications can automatically track your items’ movement and transfer the data to an ERP or financial management system. As a result, they can eliminate the need for manual form filling and obsolete spreadsheets. Fixed readers at crucial points can save you even more time, and on a production line, for example, can eradicate the need for manual intervention.
- Radio-frequency identification is ideal for complex or customized manufacturing processes because it can identify individual items or components. For example, it can ensure that precise moulds are filled with the correct volume of liquids and fired for the precise time duration or that materials are placed on the right production line. This precision helps to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
- When RFID is used to capture data on many things simultaneously, it prevents transcription errors, duplication of data, and “missing items” because data is collected and uploaded electronically. The usage of cloud-based solutions allows everyone to see the most up-to-date information on item location and status.
RFID’s Anticipated Growth
The global RFID market is expected to be worth USD 10.7 billion between 2021 and USD 17.4 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 10.2%. Factors driving the growth of the RFID market are:
- Growing market competitiveness, resulting in the availability of cost-effective RFID solutions.
- High returns on investment (ROI).
- Increasing regulations and government initiatives for various industries.
- Increased installation of RFID systems in manufacturing units to improve productivity due to COVID-19 are all driving the growth of this market.
Where Does Radio-Frequency Identification Go Next?
RFID may now be ready for its moment in the spotlight, thanks to higher accuracy rates, reduced costs, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
In a rush of high-profile trial projects in the early 2000s that didn’t seem to pan out, radio frequency identification may have been ahead of its time. It’s inaccurate to state that RFID technology has vanished; rather, it is making a comeback.
Companies are again considering tagging trucks, pallets, cases, and objects to track position and other data such as temperature and impacts, thanks to developments in sensor and data processing technologies.
Conclusion
Radio-frequency identification will provide increased management information for planning and operational purposes for your business, since it allows data to be recorded in real-time at various phases of an asset’s or product’s lifecycle. This information is valuable in enhancing business efficiency.
FAQ
It stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a type of identification using radio waves.
In supermarkets, this technology can help retailers manage and track their inventory. RFID tags can alert store employees when shelves are empty and need to be replenished or when someone has placed the wrong items on a shelf.
RFID tags are a tracking system that uses radio frequencies to locate, identify, track and communicate with objects and people. These tags are smart labels that can store a range of information, from serial numbers to a brief description to pages of data.
An RFID tag can help you find your pet the next time it goes missing and is also useful in tracking personal belongings, items, and even cars.