Wondering what’s the real difference between condition-based maintenance and predictive maintenance? Many maintenance professionals find themselves confused when trying to distinguish between these two proactive maintenance strategies. Both aim to prevent equipment failures before they occur, but they operate in fundamentally different ways. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down how condition based maintenance vs predictive maintenance differ, which industries benefit most from each approach, and how to implement the right strategy for your business.
Key Facts
- Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of equipment condition, while predictive maintenance uses data analytics and AI to forecast future failures.
- Predictive maintenance can detect potential issues weeks or months before failure, compared to condition-based maintenance, which typically identifies problems days or weeks ahead.
- ToolSense’s Asset Operations Platform combines IoT sensors with powerful analytics to enable both condition-based and predictive maintenance strategies through a single, user-friendly interface.
Maintenance Strategies: The Evolution from Reactive to Predictive
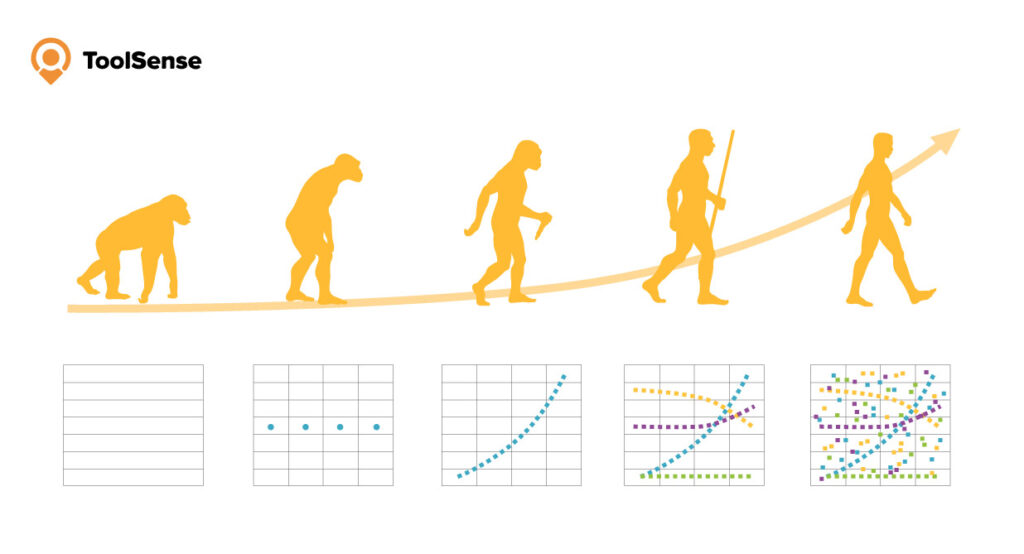
The way businesses approach equipment maintenance has evolved significantly over the decades. Traditional reactive maintenance (fixing things after they break) leads to costly downtime and emergency repairs. This led to the development of preventive maintenance, where services are performed at set intervals regardless of equipment condition.
But more advanced approaches have emerged to optimize maintenance timing and costs. Condition-based maintenance and predictive maintenance represent the cutting edge of maintenance strategies, offering ways to perform maintenance exactly when needed – not too early (wasting resources) and not too late (risking failure).
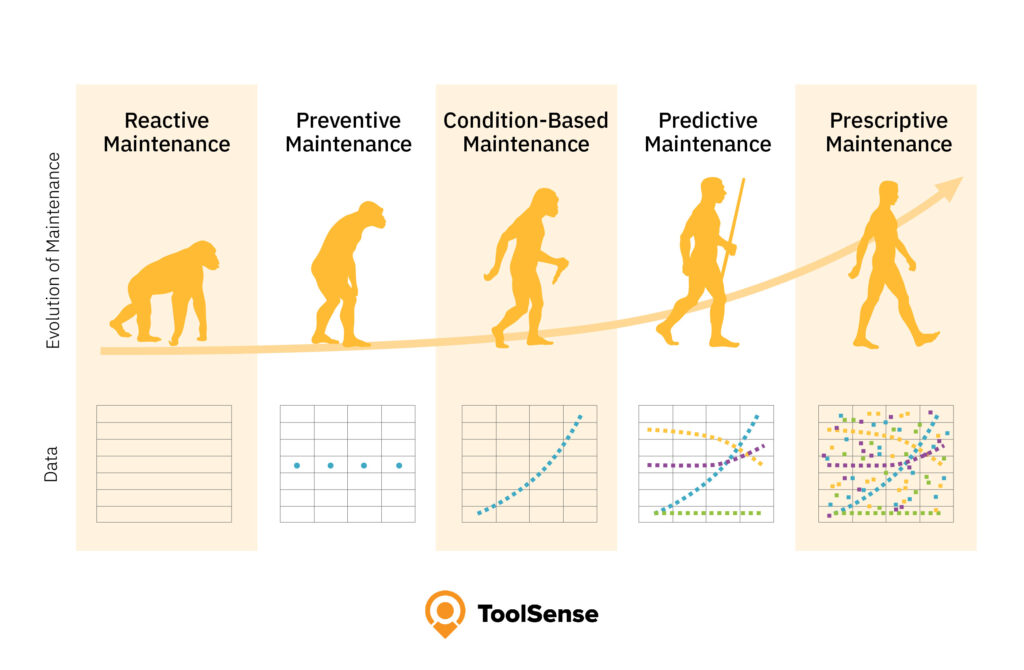
While both strategies aim to move from reactive to proactive maintenance, they take different approaches to achieve this goal. Understanding these differences is crucial for implementing the right maintenance strategy for your specific business needs.
Condition-Based Maintenance: The Essentials
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) is a maintenance strategy that monitors the actual condition of an asset to decide what maintenance needs to be done. CBM dictates that maintenance should only be performed when certain indicators show signs of decreasing performance or upcoming failure.
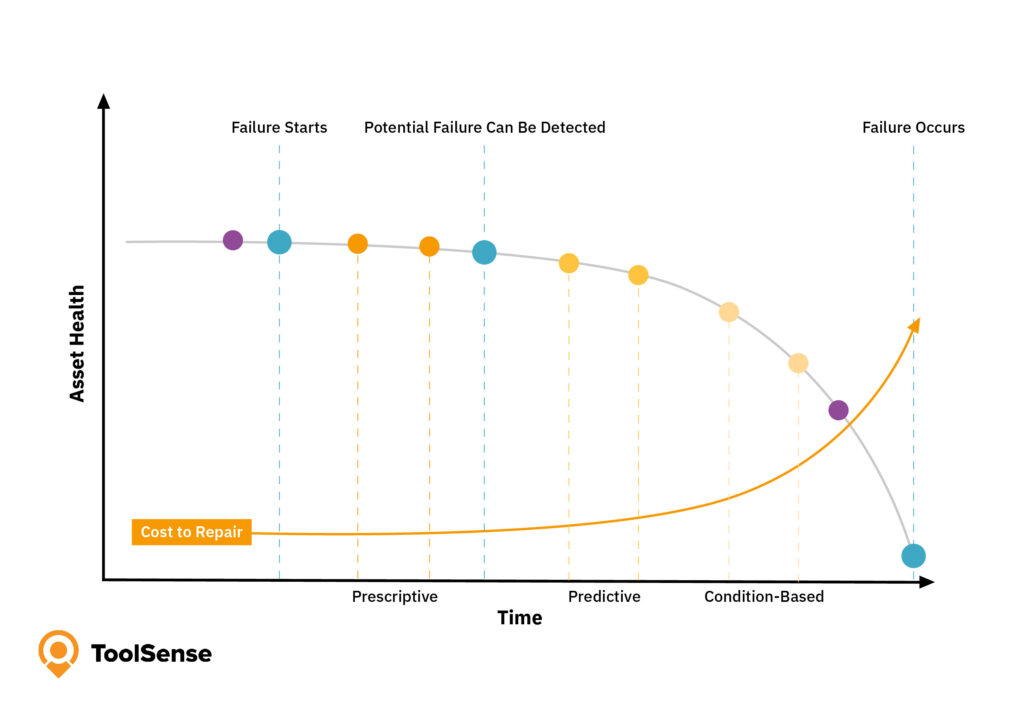
Here’s how condition based maintenance works:
- Monitoring Equipment Condition: Using sensors, gauges, or visual inspections to track equipment parameters like temperature, pressure, vibration, or oil analysis.
- Setting Thresholds: Establishing baseline parameters that indicate when an asset requires attention.
- Triggering Maintenance: When monitored parameters exceed the predetermined thresholds, maintenance work is scheduled.
For example, if you manage a fleet of construction vehicles, instead of changing the oil every 5,000 kilometers, a condition-based approach would monitor oil quality in real-time. When sensors detect that oil quality has degraded beyond an acceptable threshold, only then would maintenance be triggered.
The key advantage of condition-based maintenance is that it allows organizations to perform maintenance only when actually needed, avoiding both unnecessary maintenance and unexpected breakdowns. However, it primarily focuses on current conditions rather than predicting future failures.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



Predictive Maintenance: Advanced Data-Driven Approach
Predictive maintenance (PdM) takes condition monitoring to the next level by incorporating advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and historical data to predict when equipment failure might occur. Rather than just reacting to current conditions, predictive maintenance uses sophisticated algorithms to forecast future equipment behavior.
Here’s what makes predictive maintenance different:
- Data Collection and Integration: Combines multiple data sources, including IoT sensors, operational history, environmental factors, and more.
- Pattern Recognition: Uses algorithms to identify patterns that precede failure, often detecting subtle changes that human analysts might miss.
- Failure Prediction: Estimates when failure is likely to occur, allowing maintenance to be scheduled at the optimal time.
- Continuous Learning: The system becomes more accurate over time as it accumulates more data about equipment performance.
Consider a manufacturing plant with critical production equipment. With predictive maintenance, sensors continuously monitor multiple parameters like motor vibration, temperature, power consumption, and output quality. The predictive system analyzes this data against historical patterns and can predict a potential bearing failure weeks before it would be detected by traditional methods.
What sets predictive maintenance apart is its ability to provide a longer planning horizon. While condition-based maintenance might alert you that something needs attention now or very soon, predictive maintenance can forecast issues far in advance, allowing for better maintenance scheduling and resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Condition Based Maintenance vs Predictive Maintenance
While both maintenance strategies rely on equipment monitoring and aim to optimize maintenance timing, several key differences distinguish them:
| Feature | Condition-Based Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
| Time Horizon | Focuses on present equipment condition; typically provides days to weeks of advance warning | Projects future equipment status; potentially provides weeks to months of advance warning |
| Technology Requirements | Requires basic sensors and monitoring equipment that trigger alerts when thresholds are exceeded | Requires sophisticated data analytics platforms, machine learning algorithms, and integrated data systems |
| Data Utilization | Uses current sensor readings compared against thresholds | Analyzes historical trends, integrates multiple data sources, and applies complex algorithms to forecast outcomes |
| Implementation Complexity | Relatively straightforward to implement with direct measurement of equipment parameters | More complex, requiring data infrastructure, algorithm development, and system integration |
| Cost Structure | Lower initial investment but may have higher long-term costs if maintenance isn’t optimally timed | Higher initial investment in technology and expertise, but potentially higher ROI through optimized maintenance timing |
| Accuracy Over Time | Maintains consistent accuracy based on sensor quality and threshold settings | Improves over time as the system learns from more data and outcomes |
| Decision Trigger | Triggered when parameters exceed predetermined thresholds | Triggered by algorithmic predictions of future failure based on pattern recognition |
| Maintenance Planning | Typically requires quick response once thresholds are exceeded | Allows for longer-term planning and optimal scheduling of maintenance activities |

For many businesses, the choice between condition-based maintenance vs predictive maintenance often comes down to balancing the available resources against the criticality of the equipment being maintained. Assets with high downtime costs often justify the additional investment in predictive technologies.
Which Industries Benefit Most from Condition Based Maintenance vs Predictive Maintenance?
Different industries have unique maintenance requirements based on their equipment types, operational demands, and downtime costs. Here’s how various sectors typically leverage these maintenance strategies:
Condition-Based Maintenance Works Well For:
- Construction: Monitoring hydraulic systems on heavy equipment to prevent critical failures during operation.
- Facility Management: Tracking building system performance to ensure comfortable working environments.
- Small to Medium Manufacturing: Following equipment health without investing in extensive data infrastructure.
- Transportation: Monitoring vehicle components like brakes and engines to ensure safety and reliability.
- Food and Beverage: Ensuring production equipment maintains proper operating parameters for quality control.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



Predictive Maintenance Delivers Highest Value For:
- Large-Scale Manufacturing: Preventing costly production line shutdowns through advanced failure prediction.
- Energy and Utilities: Maintaining critical infrastructure like power generation and distribution equipment.
- Aviation: Ensuring aircraft component reliability and safety through sophisticated analytics.
- Healthcare: Maintaining critical medical equipment with minimal disruption to patient care.
- Mining: Keeping heavy equipment operational in remote locations where repairs are especially challenging.
How ToolSense Combines Condition-Based and Predictive Maintenance
As maintenance strategies continue to evolve, modern asset operations platforms like ToolSense are bridging the gap between condition-based and predictive maintenance, allowing organizations to implement the right strategy for each asset type within a unified system.

ToolSense’s Asset Operations Platform combines several key capabilities that enable effective maintenance management:
- Comprehensive Asset Tracking: Maintain a complete digital record of all your equipment, accessible via simple QR codes attached to each asset.
- IoT Integration: Connect your assets with state-of-the-art IoT hardware to monitor crucial parameters in real-time.
- Flexible Maintenance Rules Engine: Create custom maintenance workflows triggered by time intervals, usage metrics, or condition thresholds.
- Advanced Analytics: Leverage accumulated data to identify patterns and predict potential failures before they occur.
- Mobile Accessibility: Access all asset information, report issues, and manage work orders from anywhere using a smartphone app.
This integrated approach allows organizations to start with simpler condition-based maintenance strategies and gradually incorporate more predictive elements as they collect more data and become more sophisticated in their maintenance operations.
By implementing ToolSense’s Asset Operations Platform, organizations can:
- Reduce maintenance costs by 20-30%
- Decrease unplanned downtime by up to 75%
- Extend asset lifespans substantially
- Optimize maintenance team productivity
Conclusion: Implementing the Right Maintenance Strategy for Your Business
When evaluating condition based maintenance vs predictive maintenance for your organization, remember that these aren’t mutually exclusive strategies. Many successful maintenance programs combine elements of both approaches, applying more sophisticated predictive techniques to critical high-value equipment while using simpler condition-based monitoring for less critical assets.
The key is to match your maintenance strategy to your business needs, considering factors like:
- Equipment criticality and failure impact
- Available budget for maintenance technology
- Technical capabilities of your maintenance team
- Integration with existing systems and processes
For many organizations, the best approach is to start with basic condition monitoring for critical assets and gradually build toward more predictive capabilities as you collect data and gain experience. Platforms like ToolSense make this evolution easier by providing a scalable foundation that grows with your maintenance program.
Whatever stage of maintenance maturity your organization is at, moving from reactive to more proactive approaches will yield significant benefits in equipment reliability, maintenance cost optimization, and operational efficiency.
Ready to transform your maintenance strategy? Start your free 30-day trial of ToolSense today and discover how an integrated asset operations platform can help you implement the optimal maintenance strategy for your business.
FAQ
Preventive maintenance follows a fixed schedule based on time or usage, while condition-based maintenance is performed only when monitoring indicates it’s needed. Condition-based maintenance reduces unnecessary maintenance activities by focusing only on equipment showing signs of potential failure, rather than servicing all equipment on a fixed schedule.
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) relies on actual equipment condition data to trigger maintenance, while Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) performs maintenance at fixed intervals regardless of condition. CBM responds to the actual state of the equipment rather than following a calendar, potentially reducing unnecessary maintenance while still preventing failures.
A condition based maintenance workflow relies on real-time monitoring systems that alert maintenance personnel when equipment parameters exceed predetermined thresholds, prompting immediate maintenance tasks. In contrast, a predictive maintenance workflow employs advanced analytics to forecast future failures, allowing teams to schedule maintenance efforts more proactively. While both aim to optimize when to perform maintenance tasks, predictive maintenance provides longer lead times for planning, while condition-based approaches respond to current equipment conditions.
For condition-based maintenance, maintenance personnel need training in monitoring equipment, interpreting sensor data, and performing maintenance tasks when parameters exceed thresholds. For predictive maintenance, staff require additional skills in data analysis, understanding algorithmic predictions, and planning maintenance efforts based on forecasted failures rather than current conditions. In both cases, technical expertise with the specific equipment is essential, but predictive maintenance demands a higher level of analytical skills and familiarity with the maintenance workflow software and systems.