What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management is the process of handling the flow of goods and services from supplier to customer. A strategic supply chain management includes planning, organising, directing, and controlling the procurement and distribution functions within an organisation to meet customer demand while maximising profitability and efficiency, and gaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- SCM is the management of all activities involved in producing and distributing goods and services.
- To keep up with the competition, companies need to have a clear vision and strategy for their supply chain, as well as the latest technology.
- In the future, further advances in artificial intelligence and increased digitalization of supply chain management are expected.
Managing your assets shouldn’t be hard. That’s why Excel, WhatsApp or Pen & Paper are not the right tools to efficiently manage your asset operations. No matter the manufacturer or type — with ToolSense you are good to go.
The History of SCM
The modern concept of supply chain management originated in the early 20th century. In 1924, Henry Ford implemented a revolutionary new system for supplying parts and materials to his automotive factories. Ford’s “just-in-time” (JIT) delivery system eliminated waste and improved efficiency. Other companies began to adopt similar strategies, and by the 1950s, SCM and modern supply chains were becoming an essential part of business operations.
SCM vs Supply Chains
It’s important to note that SCM is not the same as a supply chain. Supply chains refer to the network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers who work together to bring products to market.
SCM is the process by which the partners in those networks manage their interactions with each other.
Today, most international companies have adopted the global supply chain management model, which allows them to source materials and products worldwide.

6 Types of Supply Chain Management
1) Continuous Flow
In a continuous flow system, parts and raw materials are delivered to the production line as they are needed. There is little or no inventory on hand, and products move through the production process quickly. This type of system is best suited for high-volume businesses with little variation in product design. An excellent example of this would be an assembly line in a car factory where each worker has one specific task that contributes to the whole product being made.
2) Fast Chain
Fast chain model is a supply chain management approach that aims to improve the performance of a company in a situation when there are frequent changes in demand and/or supply. These changes can occur due to events such as seasonal swings, sudden spikes or drops, or new product launches. A good example would be the clothing industry, where new styles and designs are constantly being released.
3) Efficient Chain
This model is best suited for hypercompetitive industries where a quick response to changes in customer demand is a must. The supplier and the manufacturer must work very closely. The system relies on demand forecasting to reduce the possibility of a bullwhip effect in the supply chain.
4) Agile
The overarching idea behind agile is to embrace change, using the insight that a project changes as it unfolds. There is no need for long term planning as the customers needs and requirements will change as the product evolves so it is not feasible or practical to plan large portions of a products life-cycle in advance. A good example would be a software development company that needs to rapidly create and release updates to its product.
5) Custom-Configured
The custom-configured SCM is perfect for companies with a lot of variation in their orders. With this model, businesses can order the exact components they need when they need them. A good example would be a company that manufactures custom medical devices. Each device is made to order, so there is no standard product that can be mass produced and stored on shelves.
6) Flexible
The flexible model is best for companies with fluctuating demand for their products. This type of SCM allows businesses to add or remove resources as needed to meet the current market. A good example would be a company that sells seasonal products, such as Christmas decorations. They may not need as many employees working on production during the off-season, but they will need more people when it gets closer to the holiday season.
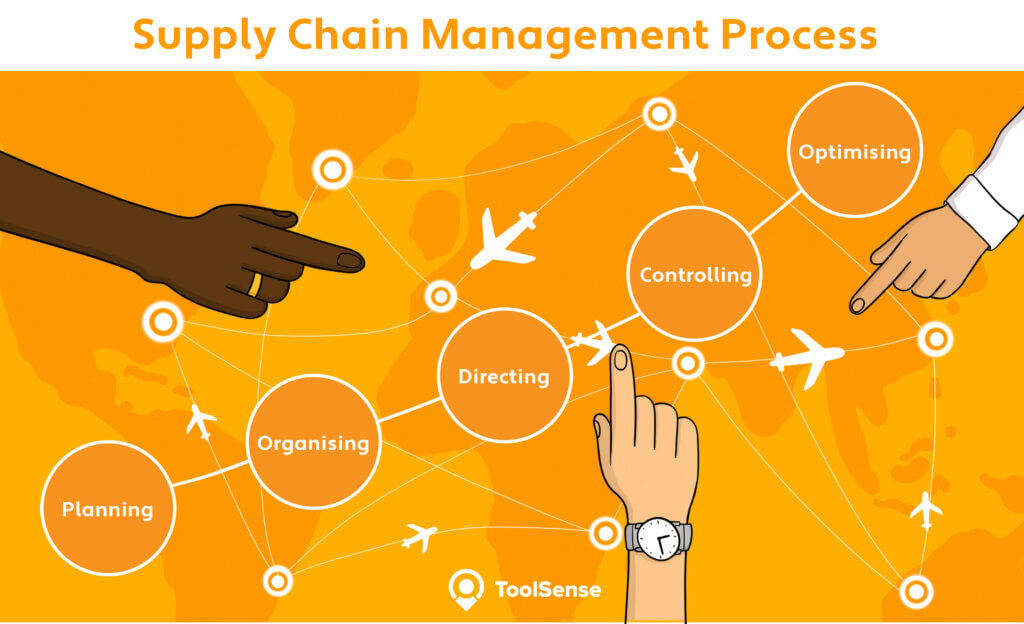
Supply Chain Management Process
The supply chain management process can be broken down into five steps:
- Planning: The supply chain manager creates a plan that outlines their goals for the SCM system and how they will achieve them. They also develop a plan for inventory management and production scheduling.
- Organising: This step involves organising the resources within the company to best support the SCM plan. This includes creating teams to manage different areas of the supply chains, such as procurement or distribution.
- Directing: The directing step is when the company assigns specific tasks to each team and provides them with clear instructions on what needs to be done.
- Controlling: The controlling step is where the supply chain manager monitors each team’s progress and ensures they are staying on track with the SCM plan.
- Optimising: The final step is to evaluate their supply chain performance and make changes as needed to improve efficiency.
6 Components of Supply Chain Management
1) Production Planning
This is the process of planning out how and when products will be produced. It includes creating a production schedule and ordering the necessary materials/components.
2) Sourcing
This is the process of finding and securing supply chain partners for the organisation. It includes negotiating prices and terms, as well as verifying that the supplier can meet the company’s quality standards.
3) Demand/Inventory Management
The inventory management process manages stock levels so that there is enough product to meet customer demand, but not too much that it goes bad or becomes obsolete. Artificial intelligence such as predictive maintenance analytics tools can help forecast demand and automate this process.
4) Production
This is the actual process of making products. It includes setting up the production line, organising workers, and overseeing the manufacturing process.
5) Logistics and Transportation
This is the process of getting products from the factory to the customer. It includes managing transportation needs, arranging for delivery and tracking orders.
6) Return of Goods
This is the process of dealing with products that customers return. It includes receiving and inspecting the product, determining why they returned it and taking corrective action if needed.
Supply Chain Management Example
The automotive industry is an excellent example of a sustainable supply chain management system. The automakers have to plan for future production years in advance, source parts from around the world, and manage an ever-changing inventory of products. They also have to deal with fluctuating demand, as consumer trends can change rapidly.
A supply chain management in construction would be different in that there is a need for a more defined communication strategy between the suppliers, contractors, and subcontractors. This will help reduce waste on the construction site and operate within the project’s timeline.
Importance of Supply Chain Management
Organisations can’t survive without a well-functioning supply chain management system. It is essential to ensure that products are available when and where needed while still maintaining a profit. In addition, an effective supply chain management system can help to:
- Reduce Costs: A well-organised or computer based supply chain management system can help reduce costs by streamlining production processes and minimising waste.
- Improve Efficiency: By optimising their global supply chain, companies can improve their efficiency and become more competitive in the international markets.
- Enhance Customer Service: Good logistics and transportation can help to ensure that customers receive their orders on time and in perfect condition.
- Respond Quickly to Changes: A well-run SCM system can help a company quickly adapt to changes in the market or environment.
Key Features of Effective Supply Chain Management
1) A Clear Vision and Strategy
Companies need a clear vision and strategy for their supply chain to manage it effectively. This should include goals for efficiency, cost reduction, and customer service.
2) Use of Technology
A sound SCM system should take advantage of the latest technology, including computers and equipment management software. Machine learning and predictive analytics can help automate many of the tasks involved in SCM.
3) Real-time and Collaboration Capabilities
The system should have the ability to provide real-time updates and collaborate with other members of the supply chain.
4) Scalability
The system should be able to adapt and scale up or down as needed to meet the changing demands of the market.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



Advantages of Supply Chain Management
- Improved Quality Control: Companies can ensure better quality control by having a system in place that tracks products from beginning to end.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Good logistics and transportation can help to ensure that customers receive their orders on time and in perfect condition.
- Improved Cash Flow: Having a well-run SCM system can help to improve cash flow by reducing inventory costs and waste.
- Improved Risk Mitigation: An effective supply chain risk management can help identify and mitigate risks before they become a problem.
Disadvantages of Supply Chain Management
- Higher Costs: Implementing a supply chain management system can be expensive, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs.
- Complexity: The global supply chain is becoming increasingly complex, making it difficult for some organisations to keep up.
- Lack of Control: Some companies lose control over their supply chain as it becomes more complex and global.
- Fragility: If any part of the supply chain breaks down, it can cause serious problems for the company.
Industry 4.0 and SCM
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is a term that has been coined to describe the current state of automation and digitisation in manufacturing. It includes technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, the internet of things (IoT), machine learning and additive printing. Many experts believe that Industry 4.0 has significantly impacted supply chain management, with companies forced to adapt their systems to create smart factories.
The Future of SCM
We can expect to see even more digitisation in supply chain management in the future. This will include blockchain technology, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, which will help automate many tasks and improve efficiency. We will also see a move towards more collaborative systems like cloud computing, where companies can share information and work together to meet the needs of their customers.
Conclusion
Supply chain management is a vital part of any business, and it is becoming increasingly complex as the world becomes more digital. Companies must have a clear vision and strategy for their global supply chains, as well as the latest technology in order to keep up with the competition.
FAQ
Supply chain management is a system that involves the planning, organising, and management of all activities involved in the production and distribution of goods and services.
Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for goods or services.
The 6 types are continuous flow, fast chain, efficient chain, agile, custom-configured and flexible.
The 6 components are planning, sourcing, production, transportation, inventory management and order returns.
Common examples of supply chain activities can include designing, manufacturing, packaging, or transporting.
Supply chain managers monitor and control every phase of the production flow, from the purchase of raw materials to the delivery of the final product.