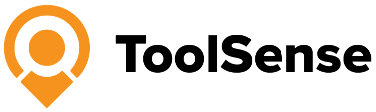In maintenance management, understanding when assets might fail is essential for preventing costly downtime and optimizing operational efficiency. Two of the most important key failure metrics in this regard are MTTF vs. MTBF – Mean Time to Failure and Mean Time Between Failures – which help in understanding the failure rate of assets. While both metrics measure aspects of asset reliability, they apply to different types of assets and provide distinct insights into asset performance.
This article will explain the differences between MTTF and MTBF, their significance in maintenance processes, and how a solution like ToolSense can simplify tracking these metrics to improve asset management and reliability.
Key Facts
- MTTF and MTBF are essential for maintenance planning: MTTF provides lifespan estimates for non-repairable assets, while MTBF helps schedule preventive maintenance for repairable assets.
- ToolSense simplifies asset tracking: The platform consolidates MTTF vs. MTBF data, automating calculations and helping teams stay proactive.
- Proactive strategies minimize downtime: Tracking MTTF and MTBF with ToolSense supports cost-effective maintenance, reduced downtime, and improved asset reliability.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



Understanding Failure Metrics
In the realm of IT service management, failure metrics are indispensable tools that provide deep insights into operational performance and highlight areas for continual improvement. These metrics help teams pinpoint vulnerabilities within the IT infrastructure and evaluate their responses to failure events. Failure analysis is a critical component of this process, enabling teams to investigate the root causes of failures and implement corrective actions.
By diligently tracking failure metrics, organizations can refine their maintenance processes, predict and manage system failures, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Failure metrics serve as key performance indicators that guide service management strategies, ensuring that systems remain reliable and responsive. They enable teams to adopt a proactive approach to maintenance, addressing potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. This not only improves the reliability of IT services but also supports the seamless operation of business activities.

Common Failure Metrics
In the world of maintenance operations, common failure metrics are indispensable for measuring performance and identifying areas for improvement. These metrics include Mean Time To Repair (MTTR), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Mean Time To Failure (MTTF), and Mean Time To Respond (MTTR). Each of these metrics offers unique insights into the performance of maintenance operations and helps track and analyze maintenance metrics effectively.
- Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) measures the average time required to repair a failed asset and restore it to operational capability. This metric is crucial for understanding the efficiency of repair processes and minimizing downtime.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), as discussed earlier, indicates the average time between failures for repairable assets, providing insights into their reliability and helping schedule preventive maintenance.
- Mean Time To Failure (MTTF), also previously covered, measures the average lifespan of non-repairable assets, aiding in replacement planning and inventory management.
- Mean Time To Respond (MTTR) tracks the average time taken to respond to a failure incident. This metric is vital for assessing the responsiveness of maintenance teams and improving incident management.
What Is MTTF?
Mean Time to Failure (MTTF) is a metric that measures the average lifespan of non-repairable assets. Unlike repairable items, which can be fixed and returned to service after a product or system failure, non-repairable assets are replaced once they fail. For these types of assets, MTTF serves as an essential predictor of how long they will function under standard operating conditions.

For instance, a light bulb is a classic example of a non-repairable item. When it fails, it’s discarded and replaced with a new one. Knowing the MTTF of such items helps maintenance teams with lifespan prediction and plan replacements effectively, reducing the risk of unexpected failures that could disrupt daily operations.
To calculate MTTF, the total operational hours of identical assets are divided by the number of failures. For example, if a company uses 100 light bulbs that collectively operate for 10,000 hours before they all burn out, the MTTF is calculated as 10,000 hours. This value tells the team that, on average, each bulb will last for about 100 hours, allowing them to plan replacements accordingly.

With ToolSense, monitoring MTTF becomes even more efficient. The platform automatically logs asset data and operational hours, calculating MTTF without the need for manual tracking. Real-time data on asset performance helps teams anticipate when replacements will be needed, ensuring they stay ahead of potential failures. ToolSense’s tracking capabilities enable maintenance teams to manage assets proactively, resulting in reduced downtime and optimized asset utilization.
What Is MTBF?
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a metric that applies to repairable assets, representing the average time between failures for a given piece of equipment. Unlike MTTF, which applies to non-repairable assets, MTBF is crucial for items that can be fixed and returned to service after a system failure. This metric gives maintenance teams insights into the reliability of equipment and helps them anticipate when maintenance is needed.
In practical terms, MTBF is the total operational time divided by the number of failures. For example, if a machine operates continuously for 1,000 hours but breaks down five times within that period, its MTBF is calculated as 200 hours. This value indicates that, on average, the machine runs for 200 hours before requiring a repair. MTBF provides a valuable forecast that maintenance teams can use to develop preventive maintenance schedules, allowing them to address issues before they lead to unexpected downtime.
The benefits of MTBF extend beyond simple failure prediction. This metric helps teams measure the effectiveness of their maintenance strategies by providing data on how long assets can operate reliably. A high MTBF generally indicates that equipment is dependable and well-maintained, while a low MTBF suggests frequent breakdowns that may need attention. By analyzing MTBF data, teams can pinpoint assets that require more frequent maintenance, make informed decisions on spare parts stocking, and even identify assets that may be more cost-effective to replace than to repair frequently.
ToolSense enhances MTBF tracking by automatically logging each asset’s operational hours and recording any failures. This automated tracking simplifies data collection, eliminating the need for manual calculations and providing real-time insights into asset reliability. ToolSense’s platform allows teams to set up maintenance reminders based on MTBF data, ensuring that preventive maintenance is scheduled at optimal intervals. By using ToolSense, teams can move toward a proactive maintenance approach, improving asset reliability, reducing unplanned downtime, and ultimately optimizing operational efficiency.
Key Differences and Importance in Preventive Maintenance
While MTTF and MTBF both measure aspects of asset performance, they apply to different types of assets and provide distinct insights that support effective maintenance planning.
Here’s a breakdown of the Pros and Cons of each metric:
| Metric | Pros | Cons |
| MTTF | Supports planning for non-repairable asset replacementAids in inventory and budgeting for replacements | Limited to non-repairable items onlyDoesn’t provide insights into repair needs |
| MTBF | Enables preventive maintenance schedulingReduces unplanned downtimeImproves asset reliability | Only applies to repairable assetsRequires continuous monitoring and logging |
Both MTTF and MTBF are integral to a comprehensive maintenance strategy, guiding decisions on asset replacements and repair schedules.
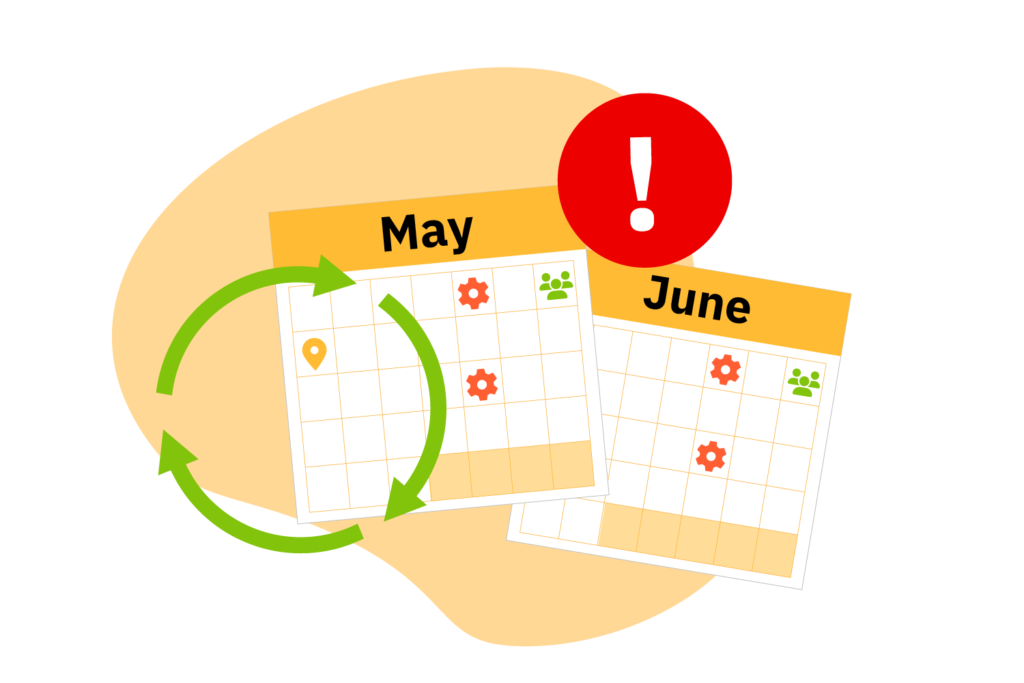
MTTF focuses on non-repairable assets and calculates the average time before these items fail permanently, while other failure metrics like MTBF measure the reliability of repairable assets. This metric is essential for planning replacements and managing inventory for disposable parts like light bulbs or batteries. By tracking MTTF, maintenance teams can predict when these items will need replacement, avoiding unexpected disruptions.
MTBF, by contrast, measures the reliability of repairable assets, indicating the average time between failures. This metric is invaluable for scheduling preventive maintenance and improving operational efficiency. MTBF tracking enables teams to proactively address repair needs, reducing emergency repairs and minimizing costly unplanned downtime.
How ToolSense Enhances Maintenance with MTTF and MTBF
With ToolSense, both MTTF and MTBF tracking are simplified and consolidated into a single dashboard. ToolSense’s automated tracking allows teams to view real-time data on asset performance and failure trends. This helps maintenance teams organize preventive maintenance schedules, monitor asset life cycles, and stay proactive, reducing downtime and optimizing costs.

Practical Tips to Improve MTTF and MTBF Maintenance Metrics with ToolSense
Improving MTTF and MTBF is key to a successful maintenance strategy, and tracking these maintenance metrics can lead to even greater asset longevity and reliability. While MTTF and MTBF metrics provide a solid foundation for maintenance planning, implementing practices to enhance these metrics can lead to even greater asset longevity and reliability. ToolSense offers powerful tools that make it easy to apply these practices and track progress over time.
1. Regular Preventive Maintenance
One of the most effective ways to improve MTBF is through regular preventive maintenance. Scheduling inspections and routine maintenance based on MTBF data helps to catch potential issues before they lead to breakdowns. ToolSense simplifies this by setting reminders and logging maintenance tasks, ensuring nothing is missed and enabling maintenance teams to optimize asset uptime.
2. Proactive Replacement of Non-Repairable Assets
For non-repairable assets, MTTF tracking allows teams to predict replacement needs accurately. Using ToolSense’s platform, maintenance teams can monitor the lifespan of these assets, ensuring replacements are planned and readily available. This proactive approach prevents unexpected disruptions and helps control replacement costs.
3. Data-Driven Decision-Making
ToolSense provides real-time data and analytics, which can guide data-driven decisions to extend asset life. For instance, if MTBF data shows that certain repairable assets fail frequently, maintenance teams can investigate the root cause. This might involve re-evaluating repair protocols or investing in higher-quality components. Similarly, MTTF data on non-repairable assets helps in identifying brands or models with better reliability, supporting long-term cost savings.
4. Efficient Spare Parts Management
Both MTBF and MTTF improvements rely on having the right parts available when needed. With ToolSense, teams can track inventory levels and associate specific parts with the assets they serve. This ensures that maintenance teams have quick access to parts, minimizing delays and reducing downtime during repairs.
5. Training and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)

Improving MTBF and MTTF also involves investing in team skills and clear procedures. Well-trained staff can execute maintenance tasks more efficiently and recognize early signs of wear or failure. ToolSense helps by providing a centralized location for storing SOPs, checklists, and training materials, ensuring every team member follows best practices consistently.
Conclusion – Maximizing Reliability with MTTF, MTBF, and ToolSense
In summary, MTTF and MTBF are essential metrics that provide critical insights into asset reliability and maintenance needs. MTTF applies to non-repairable assets, estimating their operational lifespan to guide replacement planning, while MTBF is used for repairable assets, helping maintenance teams predict the intervals between failures.
Both metrics play distinct roles in a comprehensive maintenance strategy, allowing teams to anticipate asset needs, reduce downtime, manage costs effectively and avoid unexpected breakdowns. With a platform like ToolSense, tracking MTTF and MTBF becomes seamless. ToolSense’s automated tracking, real-time data, and centralized dashboard support proactive maintenance strategies, helping teams optimize asset performance, manage inventory efficiently, and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Leveraging these metrics with ToolSense empowers companies to create a more reliable, cost-effective maintenance operation.
FAQ
The main difference is that MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) applies to repairable assets and measures the average time between breakdowns. MTTF (Mean Time to Failure) is used for non-repairable assets and estimates their average lifespan before they fail and need replacement.
To calculate MTBF, divide the total operational time by the number of failures. For MTTF, divide the total operational time of identical assets by the number of assets that failed.
MTTF and MTBF reliability indicate an asset’s expected lifespan (MTTF) and how often it is likely to fail (MTBF), helping teams maintain equipment more predictably.
MTTF estimates lifespan for non-repairable assets; MTTR (Mean Time to Repair) measures the average repair time for failures; and MTBF predicts the time between failures for repairable assets. Together, these metrics offer a complete view of availability and maintenance needs.