Who hasn’t felt the sting of an unexpected equipment breakdown, disrupting not only the workflow but also impacting the budget? Picture this: a well-oiled machine humming along smoothly, with each part playing its role flawlessly. That’s the power of the right maintenance strategy. And with that in mind, the question arises: what are the right types of maintenance?
Whether it’s the preventive care of regular check-ups or the swift response of corrective action, each approach holds its unique charm. But how do you decide which one fits your business puzzle perfectly? Consider this: preventive maintenance is like your regular health check-up, quietly averting crises, while reactive maintenance jumps in like an emergency response team. Urgent or emergency maintenance, on the other hand, occurs after total equipment failure, requiring urgent and costly repairs. Choosing wisely could mean the difference between a minor hiccup and a full-blown operational meltdown.
Different Types of Maintenance
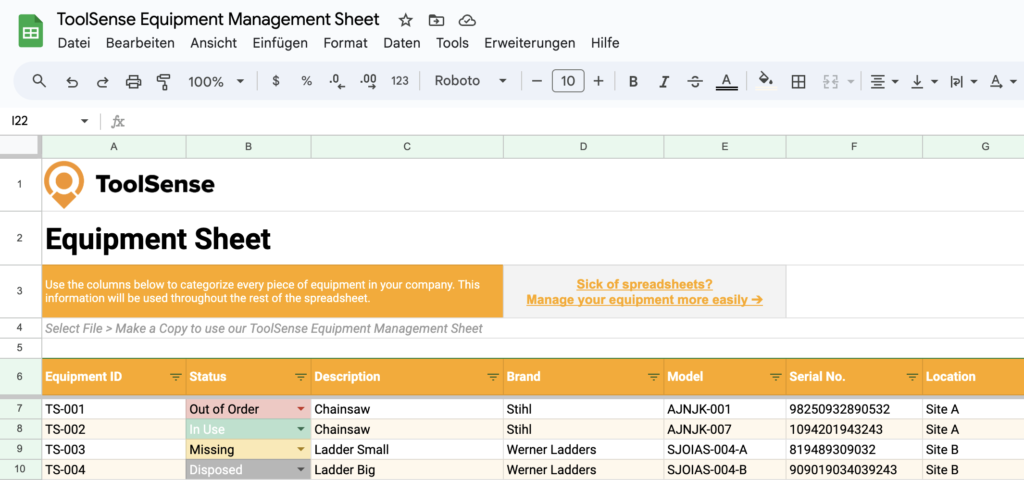
There are six general types of maintenance strategies that companies use. They are a range of proactive and reactive methodologies. Depending on how you form your business structure, maintenance can become costly or affordable, create problems or solve them. The right maintenance program is important because it determines the impact on customers and the total cost based on the investment return.
The different types of maintenance strategies include:
- Preventive maintenance – includes regular and periodic (time-based) schedules.
- Corrective maintenance – occurs when an issue is noticed.
- Predetermined maintenance – follows a factory schedule.
- Condition-based maintenance – occurs when a situation or condition indicates maintenance is needed.
- Predictive maintenance – is data-driven and impacted by preset parameters.
- Reactive maintenance – occurs when a total breakdown or failure appears.
Preventive Maintenance
Out of the six types of maintenance, preventive maintenance seeks out and repairs more minor issues and decreases the occurrence of major repairs. This type may take on aspects of all other maintenance types. For example, maintenance inspections may change based on the age of the equipment. When it is new, the procedure may be more of a predetermined maintenance style, but as it ages, more frequent inspections, both physical and through data, may prevent minor performance issues from becoming extensive and more costly repairs.
Example of Preventative Maintenance
An excellent example of preventative maintenance is the seasonal cleaning of an HVAC unit. In spring, you schedule maintenance to ensure that grit and sand are not inside the casing or leaves are not blocking the air intake. There is no specific issue, but we know that leaves can accumulate throughout the seasons and cause problems later in the year. Removing the grit or leaves prevents a later difficulty, such as poor performance, increased energy usage, etc.
Preventive maintenance is easily described as regular and routine inspections that look for wear before symptoms appear.
We all know that routine maintenance tasks are vital if you want to keep your essential equipment in top shape.
Costs of Preventative Maintenance
Expect to pay more for labour under preventative maintenance, so equipment inspections occur as scheduled. However, those added labour costs may be offset by preventing major repairs and the increase in energy consumption from machines that do not operate at peak performance. In addition, service can be outsourced, which can help reduce the cost of labour.
Benefits of Preventative Maintenance
- Prevention of major repairs.
- Keeps businesses open by preventing most emergency repairs.
- Adds to the product’s lifecycle by reducing wear.
- Keeps energy costs at their lowest possible rates.

Corrective Maintenance
Under corrective maintenance, also known as unplanned corrective maintenance, maintenance teams get to work as soon as a problem occurs. The goal of corrective maintenance is to bring systems back to regular operation as quickly as possible. With corrective maintenance, there is no program for regular maintenance. A problem must be present before maintenance occurs.
Examples of corrective maintenance include:
- Repairing a broken HVAC unit rather than maintaining it.
- Repairing an HVAC unit after data from the unit shows it is not functioning at peak performance.
Cost of Corrective Maintenance
Because there is not a regular maintenance program that prevents breakdown, maintenance occurs only when an issue is noticed. The cost of repairs may be slightly more expensive, but far cheaper than paying a crew to maintain equipment regularly. The equipment is fixed just in time, but this method can backfire if a catastrophic event happens. In the above example, the HVAC is not repairable, and replacement is the only option. Even then, some costs for replacement may be covered under warranty.
Benefits of Corrective Maintenance
- Decreased monthly maintenance costs.
- Decrease in time for managing maintenance.
- Focuses on non-critical elements.
- A more straightforward maintenance process.
ToolSense is trusted by 700+ companies



Predetermined Maintenance
Predetermined maintenance follows a plan of action created by the manufacture of equipment, rather than scheduled maintenance laid out by a maintenance team.
Examples of Predetermined Maintenance
An excellent example of predetermined maintenance is when machinery maintenance is scheduled at time intervals based on the manufacture’s recommendations. For example, oil changes will be every fourth month. Transmission service will occur at X number of hours of run time. After one year of use, Parts X, Y, and Z are checked for wear. Engine replacement occurs after X number of years.
Even if the machine has sat idle for four months, the oil is changed. The list of maintenance is scheduled based on time or usage rather than functionality. Another example is when smart data indicates a decrease in productivity. The drop in performance signals a need for maintenance. Predetermined maintenance crosses over into predictive maintenance, where data reporting for issues occurs.
Cost of Predetermined Maintenance
The cost of predetermined maintenance programs is generally low. Because everything is scheduled, you can plan for the purchasing of parts and maintenance tasks. Costs do vary based on the machinery and parts associated, but even those are known costs.
Predetermined Maintenance Benefits
- Much easier to schedule and manage, including labor.
- The manufacturer outlines the maintenance plan.
- You can schedule technicians rather than hire maintenance personnel.

Condition-Based Maintenance
As the name implies, condition-based maintenance focuses on outcomes through measurement or observation. Machines have a range of normal operating conditions. Within that range, the operation is acceptable. Near the edges of that range, maintenance may be required.
Examples of Condition-Based Maintenance
An excellent example of condition-based maintenance is that pesky check engine light in your car. When the check engine light comes on, the car’s system has indicated that something is out of the normal range and maintenance needs to be scheduled. The exact process may occur with machines that self-monitor through smart technology or physical inspections in a business.
Another example of condition-based maintenance might be when a machine begins to use more energy to function. That may be that a tank of fuel does not last as long or that there is a sudden spike in electrical usage. Again, that level of condition requires maintenance.
See How Global Facility Management Company ISS Improved Their Maintenance Management With ToolSense
Cost of Condition-Based Maintenance
The overall cost of condition-based maintenance is low. Because maintenance is scheduled when anomalies begin, the cost to correct them is less than repairing a complete failure of the machine. The benefits of conditional-based maintenance show us more.
Benefits of Condition-Based Maintenance
- Less downtime.
- Decreased energy consumption.
- Greater productivity — the equipment runs in the range of peak performance for longer.
- Fewer complete failures as equipment maintenance occur as the performance drops.

Predictive Maintenance
One of the more advanced ways to conduct maintenance tasks, predictive maintenance, is data-driven. Data supplied by the equipment indicates when maintenance is needed. Data also is a means to map when the failure of the machine may occur.
Examples of Predictive Maintenance
Technology is all around us, and many businesses put it to work for them. The examples of predictive maintenance include:
- Alarms that sound when the temperature on a machine or in an environment begins to move outside the safe parameters set up per the manufacturer’s guidelines. The internal temperature in a data center’s server room becomes too hot, and sensors in that room send out at alert.
- A sensor in an engine monitors misfires and alerts maintenance that engine service is needed.
- A sensor on a refrigeration truck monitors the internal temperatures of the truck and alerts the driver when the internal temperature falls outside acceptable parameters.
These alerts do not necessarily mean a complete failure occurs, but that condition is approaching a range where catastrophic failure can occur.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
There is a higher cost at set up for predictive infrastructure, but overall, predictive maintenance can save money by:
- Improving product quality.
- Reducing catastrophic failures.
- Improved equipment performance.
- Higher customer satisfaction.
There can also be a reduction in maintenance labor since automation can also become part of the predictive process.

Reactive (Run-to-Failure) Maintenance
Reactive maintenance, also known as urgent maintenance, is a maintenance system that responds when a failure of machinery or systems occurs. The repairs may be handled in-house or by the manufacturer, or through a combination of in-house maintenance and the manufacture’s technicians. Unlike preventive maintenance, reaction maintenance occurs when a breakdown happens.
Examples of Reactive Maintenance
The car wash at the local gas station breaks, and the maintenance team is notified. The printing press that handles varnish applications fails, and maintenance or the factory service team is notified, and repairs are scheduled.

Costs of Reactive Maintenance
The costs of reactive maintenance can range from minor repairs to total replacement of machinery. Therefore, it becomes difficult to predict the cost of reactive maintenance, though occasionally the cost is offset by a warranty or service contract.
Benefits of Reactive Maintenance
It may seem like a waste of money to not have any other type of maintenance in place before machinery or equipment fails. However, there are some cost savings associated with reactive maintenance. Those include:
- Less maintenance staff, fewer employees, fewer wages paid out regularly, etc.
- Fewer costs to implementation – no regular maintenance means no labor or part costs until failure occurs.
- Fewer management hours are needed for maintenance planning.
Managing maintenance across an entire fleet is quite a challenge. Build custom workflows in our Asset Operations Platform to easily manage maintenance processes for thousands of assets.
Best Maintenance? How to Choose the Right Strategy
Choosing the best maintenance methodology is a measurement of risk. First, look at what you lose if equipment fails. If the cost is greater than the repair, then a reactive type maintenance methodology may be perfect for your businesses. On the other hand, if the cost is higher if machinery fails, then a proactive type of maintenance methodology might be more beneficial.
Weigh in aspects such as:
- Time for maintenance to occur.
- Cost to business in terms of loss of production.
- Ask yourself: are customers impacted?
A business may also need more than one type of maintenance, depending on the nature of what they do. For example, preventative maintenance is an asset if it protects measurements such as customer satisfaction, reduces legal risks, etc. On the other hand, reactive maintenance may be more economical if the equipment is under warranty or approaching the end of its lifecycle. Regardless of which strategy you choose, maintenance management software like ToolSense can help your company automate tasks, maintain an overview and be more cost-effective.
How ToolSense Improves Your Maintenance Management
ToolSense is a comprehensive asset and maintenance management solution suitable for small and large companies in all industries. The cloud-based system is available as a desktop application as well as a mobile app, allowing employees to access vital information from anywhere and enabling better communications between desk workers and maintenance staff.
Once your assets are imported, they receive an individual lifecycle folder that stores all data related to the machine or tool, such as usage, downtime, maintenance history, warranty information, instructions, photos, videos, and more. Because everything is kept in one place, employees always know where to look for information, which saves time during the maintenance process.
ToolSense also offers the ability to create custom maintenance checklists, ensuring that maintenance tasks are carried out diligently and precisely. Additionally, you can set up individual maintenance reminders for each asset – either based on a certain date or the machine’s collected IoT data. That way, ToolSense will remind you when a certain maintenance task is due, ensuring that important audits are not forgotten.
The software’s work order management tools create a smoother maintenance workflow, regardless of the type of business or the employees’ location. By scanning a QR code attached to a machine or asset, workers can report a problem or request a spare part in just a few clicks. The work order will then be forwarded to the responsible employee, either through the app or an e-mail notification. ToolSense also offers useful reporting and analytics features that will allow you to implement a predictive maintenance schedule based on your assets’ data.
Regardless of the Type of Maintenance: What are Good Maintenance Practices?
Good maintenance practices are essential to ensure the longevity, efficiency, and safety of equipment. Implementing these practices can help prevent unexpected breakdowns, optimize performance, and reduce overall maintenance costs. Here are some good maintenance practices that can be integrated with the various types of maintenance discussed earlier:
- Regular Inspections and Checkups: Routine inspections are vital for identifying potential issues before they escalate. This aligns well with preventive maintenance, where regular check-ups can help avert crises.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Establish a maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations or operational needs, as seen in predetermined maintenance. This ensures that maintenance tasks are performed at optimal intervals.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and replacements. This documentation helps track the equipment’s history and can be crucial for condition-based maintenance.
- Use of Technology: Leverage maintenance management software, such as ToolSense, to streamline maintenance processes. These tools can automate scheduling, track maintenance history, and monitor equipment conditions in real-time.
- Predictive Analytics: Implement predictive maintenance by using data and advanced analytics to forecast when maintenance should be performed. This practice helps in reducing downtime and preventing major failures.
- Training and Skill Development: Ensure that maintenance personnel are well-trained and updated with the latest techniques and safety protocols. Skilled workers can perform maintenance tasks more efficiently and safely.
- Spare Parts Management: Maintain an adequate inventory of spare parts to ensure quick repairs and minimize equipment downtime. This practice is particularly important for corrective maintenance when immediate repairs are needed.
- Safety Compliance: Adhere to all relevant safety regulations and standards to ensure a safe working environment. Regular safety inspections and compliance checks are crucial components of a comprehensive maintenance program.
- Reactive Measures: While proactive maintenance is preferred, being prepared for reactive maintenance is also important. Have a plan in place for dealing with unexpected equipment failures to minimize disruption.
By integrating these practices, businesses can enhance the effectiveness of their maintenance strategies, ensuring that equipment operates smoothly and efficiently. Using modern tools like the ToolSense Asset Operations Platform can further simplify and optimize these maintenance processes, providing a comprehensive solution for all maintenance needs.
Why Is the Right Maintenance Strategy Important?
The right maintenance strategy is crucial because it reduces risks and improves efficiency while keeping costs in an affordable range. You also have the opportunity to extend the life of your assets. That process also means reducing the cost of repairs and keeping overall productivity higher.
FAQ
Maintenance involves a set of activities aimed at keeping equipment and systems in optimal working condition. It includes: Preventive Maintenance, Corrective Maintenance, Predetermined Maintenance, Condition-Based Maintenance, Predictive Maintenance, and Reactive Maintenance. Proper maintenance is crucial for reducing risks, saving costs, ensuring safety, maintaining productivity, and extending the lifespan of assets. Modern tools like the ToolSense Asset Operations Platform can streamline maintenance management by offering features such as asset tracking and automated scheduling.
What Are the Different Types of Maintenance?
The 6 different types are; Predetermined Maintenance, Preventive Maintenance, Corrective Maintenance, Condition-based Maintenance, Predictive Maintenance and Reactive Maintenance.
Choosing the best maintenance methodology is a risk measurement. Start by looking at what you lose when equipment fails. If the cost is higher than the repair cost, then a reactive maintenance method may be ideal for your business. On the other hand, if the costs are higher in the event of a machine failure, then a proactive maintenance method might be more beneficial.
The 4 different software maintenance types are; Corrective Software Maintenance, Adaptive Software Maintenance, Perfective Software Maintenance and Preventive Software Maintenance.
The right maintenance strategy is critical because it reduces risks and improves efficiency while keeping costs within an affordable range. You also have the opportunity to extend the life of your equipment. This process also means that the cost of repairs is reduced and overall productivity remains higher.