Seeking to understand CMMS and its impact on maintenance operations? CMMS, or Computerized Maintenance Management Systems, are powerful tools designed to streamline your maintenance tasks, enhance operational efficiency, and keep your assets in prime condition. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental aspects of CMMS. We explain how these systems work, desribe their benefits, and why they are essential for efficient asset management.
Key Takeaways
- A CMMS is a sophisticated software designed to centralize maintenance information and automate operations thus improving efficiency and safety while reducing costs.
- Modern CMMS systems centralize asset information, automate maintenance tasks, provide insights into equipment performance, and optimize asset usage. They offer core features like work order and asset management, preventive maintenance, inventory management, and analytics.
- Implementing CMMS software in various industries leads to streamlined workflows, reduced downtime, improved asset management, enhanced communication, decision-making and cost savings, supporting a shift from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies.

Defining the terms: CMMS Definition
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial maintenance, the term ‘CMMS’ frequently surfaces as a beacon of progress. But what precisely is a Computerized Maintenance Management System?
What is a Maintenance Management System?
At the intersection of maintenance and technology stands the Maintenance Management System. It´s a centralized platform that orchestrates the scheduling, monitoring, and reporting of maintenance tasks. As the cornerstone of modern asset management, it enables meticulous tracking of work orders, ensuring the reliability and longevity of assets and equipment. The system’s detailed work order data serves as the lifeblood of informed decision-making, providing insights that enhance operational stability and asset health.
A Maintenance Management System is more than just a tool; it’s a strategic ally for maintenance teams. By utilizing maintenance management software, teams can access features such as:
- Work order management
- Asset management
- Preventive maintenance
- Maintenance and inventory management
It fosters a more organized approach to maintenance scheduling and asset tracking. In essence, it converts what was once a complex maze of maintenance activities into a streamlined, data-driven process that is both efficient and cost-effective.
What is CMMS? What is a CMMS System? What is a CMMS Software?
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a pivotal element within the domain of asset performance and maintenance management, offering a software-based framework that elevates traditional maintenance processes to new heights of efficiency. CMMS is a transformative force, providing real-time insights into equipment performance and maintenance needs, from its early iterations in the 1960s to today’s advanced platforms, evolving to become an essential tool for organizations aiming to automate and centralize their maintenance operations.

The value of CMMS software lies in its ability to organize, track, and diagnose assets; enhance communication; support cost-effective decision-making; manage operations across multiple locations; and ensure compliance with safety and environmental laws. Its versatility makes CMMS an indispensable asset in the pursuit of operational excellence and reduced maintenance costs. Whether referred to as a CMMS System or CMMS Software, these terms often interchangeably describe a comprehensive tool designed to centralize maintenance information and operations.
How do CMMS Systems Work?
The operation of CMMS Systems is comparable to the precision and efficiency of a clockwork mechanism in full swing. Fundamentally, a CMMS:
- Centralizes and automates maintenance tasks, equipment data, and inventory control
- Offers critical insights into equipment performance and maintenance needs
- Optimizes the use, availability, and lifespan of a myriad of assets, from machinery to fleets and beyond
It’s the technological glue that holds maintenance operations together. How does such a system achieve this level of efficiency? By meeting specific criteria that define its capabilities: Managing assets across locations; Maintaining replacement components inventory; Planning maintenance tasks; Controlling manpower and parts distribution; Providing reports on maintenance costs and asset usage; Ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations. With a CMMS, teams can bid farewell to manual spreadsheets and welcome a new era of streamlined maintenance management.
Core Functions of CMMS (Features)
Delving into the core functions of CMMS unveils a suite of features that are the cornerstone of any robust maintenance operation. A CMMS platform is comprised of:
- Work order management
- Asset management
- Preventive maintenance
- Inventory management
- Reporting and analytics
- Mobile app support
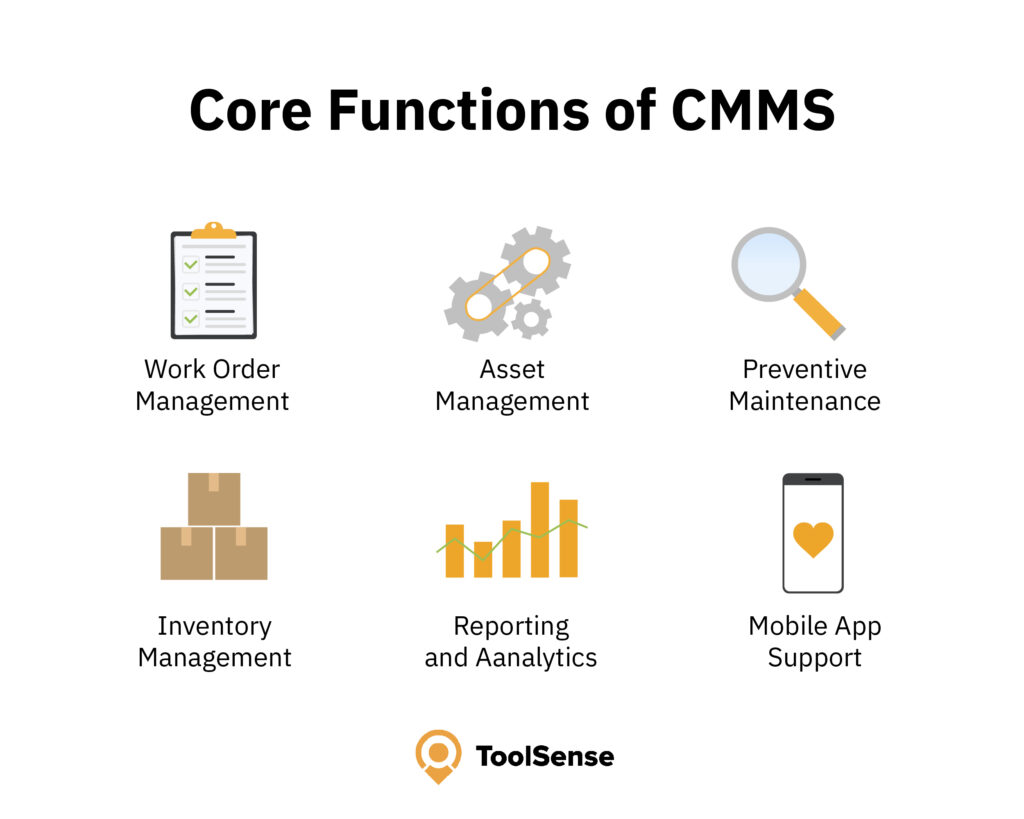
These components make up the core of the system. They are designed to boost productivity, enhance equipment performance, and eradicate the manual elements that once bogged down maintenance responsibilities. It’s the integration of these core functions that enables CMMS to transform maintenance operations into a strategic advantage for organizations.
Benefits of CMMS Implementation
The benefits of implementing a CMMS are far-reaching and impactful. Some of the key CMMS benefits include:
- Streamlined workflows
- Reduced downtime and costs
- Improved asset management
- Enhanced communication and decision-making
- Elevated operational transparency
- Optimized resource allocation
- Facilitated regulatory compliance
- Improved inventory accuracy
- Extended equipment lifespans
- Data-driven decision support
- Increased productivity
CMMS not only ensures maintenance occurs when it should but also uses data for efficient tasking and scheduling, assuring the availability of personnel and parts, and thus reducing downtime for equipment.
From minimizing equipment failure and production downtime to standardizing maintenance processes and improving compliance: With CMMS, organizations harness a tool that not only caters to the present maintenance needs but also adapts to future challenges, ensuring a continuous cycle of improvement and efficiency.
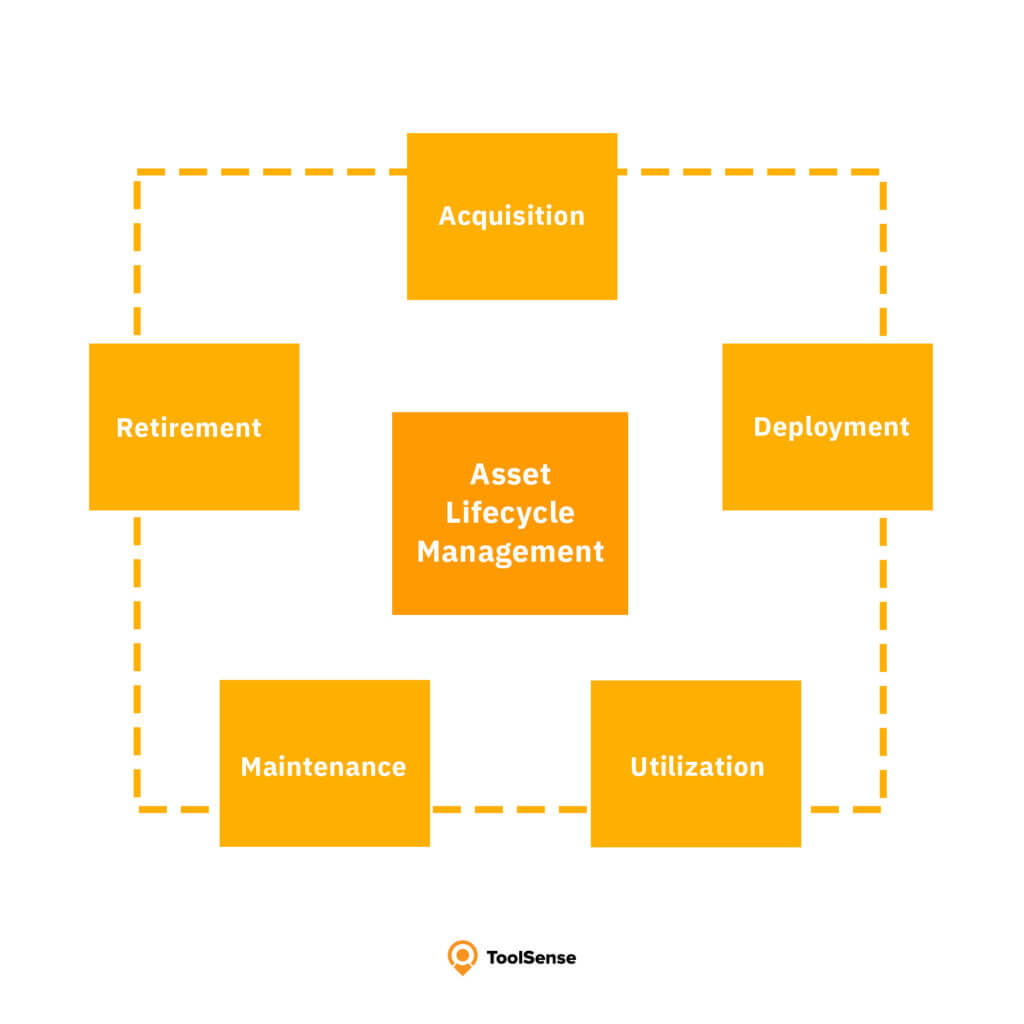
The Role of CMMS in Asset Management
In the realm of asset management, CMMS emerges as a pivotal force. It extends its capabilities beyond mere maintenance management to encompass entire asset lifecycle management, underscoring the importance of tracking an asset from acquisition to disposal. By integrating financial data from other company departments, CMMS aids in:
- reducing long-term, asset-related expenses
- improving asset performance and reliability
- optimizing asset utilization
- enhancing regulatory compliance
This underscores its role in asset lifecycle management. Leveraging CMMS for asset management provides insights into maintenance performance and asset health, which leads to enhanced operational efficiency.
It’s the meticulous tracking of assets that CMMS enables, offering up-to-date status information and accessible detailed maintenance history to ensure proper health monitoring.
Asset Tracking and Monitoring
Asset tracking and monitoring are integral components of a CMMS, centralizing asset information, maintenance history, and performance trends to enable better decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies. By identifying all assets requiring maintenance and compiling essential data within the CMMS database, organizations gain an unparalleled view of their assets, equipping them with the information necessary for effective asset management.
The power of CMMS in asset tracking lies in its ability to:
- Analyze patterns in asset breakdowns
- Effectively manage maintenance and unscheduled downtime
- Ensure that complex assets, such as those in educational institutions, are maintained with precision
- Contribute to sound decision-making that extends asset lifespans and optimizes performance
Additionally, CMMS supports maintenance teams by preserving documentation and procedures linked to assets, enabling integration with building automation systems for centralized control and improved energy efficiency.

Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle management is a critical aspect where CMMS plays a supportive role by analyzing historical maintenance data to identify patterns and trends, optimizing maintenance strategies and asset performance. This analysis enables organizations to extend asset longevity while minimizing equipment breakdowns and costs, contributing to significant long-term cost savings.
The detailed digital asset profiles maintained within a CMMS are instrumental in calculating maintenance costs and making informed decisions regarding capital investments and the repair-or-replace dilemma. It’s the proactive approach to preventive maintenance that CMMS enables, predicting potential issues and facilitating early intervention to prevent asset failure, thus supporting the entire asset lifecycle management process from pre-installation planning to decommissioning.
CMMS Best Practices: Real-World CMMS Applications in Various Industries
The utility of CMMS extends across various industries, each harnessing its capabilities to meet unique maintenance requirements. Best practices in CMMS implementation involve seeking digital solutions that enhance cost, efficiency, and safety ratings. In industries such as education, CMMS acts as an organizational hub, managing support tickets and routine maintenance for faster resolution of requests and improved cost allocation.
In the maritime sector, companies utilize CMMS solutions to manage maintenance history records and comply with maintenance requests, promoting transparency and operational efficiency. CMMS serves as a database for safety materials and inspection checklists, contributing to tracking employee health and safety. These real-world applications illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of CMMS in optimizing maintenance management operations across diverse settings.
In the following, we would like to take a closer look at the facility management industry and the construction sector as an example of best practice.
Facility Management Industry
The facility management industry greatly benefits from the integration of CMMS into its daily operations. As a field responsible for ensuring the functionality, comfort, safety, and efficiency of a built environment — such as office complexes, schools, and hospitals — facility management relies heavily on the upkeep of various systems and infrastructure. CMMS serves as a strategic partner in this sector by:
- Systematizing the tracking of maintenance requests and work order completions, providing a clear overview of tasks and their status
- Enabling facility managers to make better-informed decisions about asset procurement and lifecycle management
- Assisting in the management of vendor contracts and associated documentation
- Streamlining the process of regulatory compliance and safety checks, maintaining a safe environment for occupants
- Facilitating real-time updates and communication between maintenance teams and management
- Allowing for the scheduling of preventive maintenance to minimize the risk of system failures and extend asset life
By leveraging CMMS, facility management can transition from a reactive to a preventive and predictive maintenance model, implement energy-saving strategies by monitoring systems and identifying areas for improvement, optimize the use of space and equipment, leading to cost savings and increased operational efficiency and improve the allocation of maintenance resources, ensuring that critical infrastructure receives timely attention
This shift towards a more proactive and data-driven approach in facility management is essential for maintaining high standards of operation and occupant satisfaction. CMMS platforms, especially those with mobile or web-based capabilities, ensure that facility managers have instant access to important data and can manage maintenance activities efficiently, regardless of their location, thus enhancing the overall productivity of the maintenance team.

Construction Industry
In the construction industry, the deployment of CMMS software is pivotal for managing the vast array of equipment and machinery that is essential to project completion. CMMS assists construction managers in tracking the maintenance and service history of their equipment, ensuring that everything is operating at peak efficiency and safety standards are rigorously maintained. With the help of CMMS, construction sites can improve equipment reliability, reduce costly downtime, and adhere to tight project schedules.
Key advantages of CMMS in the construction industry include:
- Scheduling regular maintenance to prevent equipment failure on critical tasks
- Monitoring equipment usage and performance to optimize the allocation of machinery
- Keeping a comprehensive record of maintenance and repairs to support warranty claims and audits
- Enabling rapid response to equipment breakdowns with mobile access to maintenance records and work orders
- Tracking inventory of spare parts to minimize delays in repairs and maintenance
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations and standards through detailed records of inspections and corrective actions
By integrating CMMS into their operations, construction companies can gain a competitive edge through enhanced asset management, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings on projects.

EAM vs. CMMS
The debate between CMMS and EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) is a common point of confusion, transcending industry boundaries and challenging professionals to distinguish their distinct functionalities and applications. While CMMS is designed to facilitate asset maintenance management and extend equipment life, EAM offers a broader range of features that encompass the entire asset lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. CMMS streamlines maintenance tasks, equipment data, and inventory control, whereas EAM tracks, manages, and analyzes asset performance and costs on a wider scale.
CMMS platforms, with their emphasis on maintenance functions, have become increasingly popular due to their ability to organize a company’s maintenance operations, streamline procedures, and support cost-effective decision-making. EAM systems, however, provide a comprehensive view of asset management, tackling more than just maintenance concerns. They include features such as procurement, project management, and lifecycle cost analysis, making them a more extensive solution for organizations with complex asset management needs. In another article, we compared the top EAM software solutions.
Best CMMS Software
Selecting the ideal CMMS software is critical for enhancing maintenance management within your organization. This concise overview introduces the top three CMMS solutions, providing a glimpse into the detailed analysis found in our full article where we compare the top ten CMMS solutions.
- ToolSense: This all-in-one solution is lauded for its advanced workflow automation and intuitive user experience. ToolSense is particularly well-suited for industries seeking to integrate IoT capabilities into their maintenance strategies.
- MaintainX: Known for its on-the-go maintenance management, MaintainX offers a mobile-first platform that excels in real-time communication and efficient work order management, ideal for dynamic teams needing mobile access.
- UpKeep: UpKeep provides streamlined asset upkeep anywhere, featuring an accessible mobile application and a comprehensive toolkit that serves various industries, from manufacturing to hospitality.
Our in-depth article delves into the specific features, benefits, and unique aspects of the top-ranked CMMS systems. You’ll learn about user-friendly interfaces, essential maintenance management tools, integration with other systems, and the level of customer support you can expect. Discover how these leading CMMS options can revolutionize your maintenance management and enhance your team’s performance.
![Best CMMS Software Solutions [Top 10]](https://toolsense.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Best-CMMS-Software-Titelbild-ToolSense-1024x554.jpg)
Introducing ToolSense: Your CMMS Software
ToolSense emerges as a formidable CMMS software solution, tailored to meet the intricate requirements of maintenance management. It differentiates itself with features such as workflow automation, QR code-enabled problem reporting, IoT integration, and an intuitive user experience, all designed to make managing assets or equipment easier.
With ToolSense, you can set up assets within minutes, leveraging powerful rules engines to create maintenance workflows for multiple assets at once, all while ensuring that all documents are organized and accessible at all times.
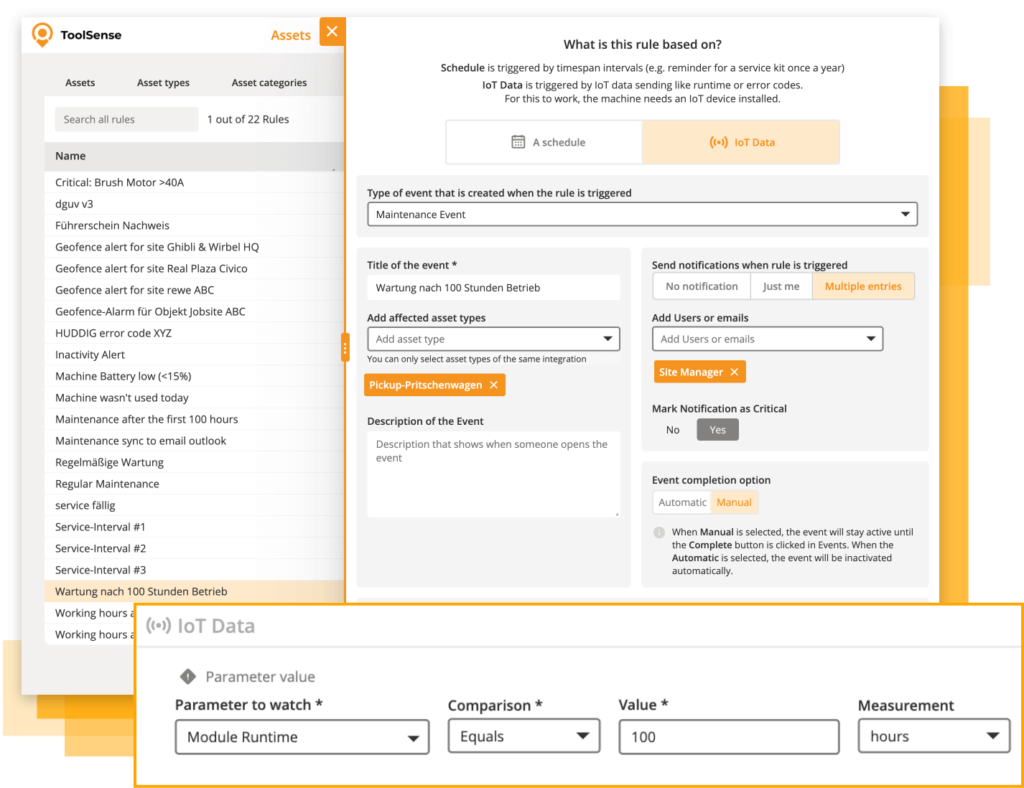
The ToolSense CMMS is a cloud-based maintenance programthat offers the following benefits:
- Eliminates the need for pen, paper, and Excel tables
- Provides a clear overview of maintenance tasks
- Significantly eases the maintenance management process
- Simplifies workflows for frontline workers
- Saves time for frontline workers
- Reduces company maintenance costs by 20%
For those interested in experiencing the efficacy of ToolSense firsthand, we offer a free 30-day trial and a free demo tour, showcasing its capabilities and potential return on investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
The primary elements of a CMMS platform encompass operator interfaces, reporting dashboards, administrative settings, and databases to effectively manage maintenance operations.
Using CMMS software offers benefits such as streamlining preventive maintenance, organizing inventory management, reducing downtime, improving cost-effectiveness, enhancing communication, and supporting compliance and safety standards. In our article we assembled a comparison of the most relevant CMMS software providers.
A mobile CMMS is a smartphone app or a browser-based software accessible for mobile devices that allows maintenance teams to manage work orders, submit requests, and access asset history and documentation on the go, leading to improved efficiency and real-time updates.
CMMS provides asset visibility by centralizing asset data in a database, offering a comprehensive view of asset health and performance, helping maintenance managers and teams make informed decisions.
CMMS focuses on automating maintenance tasks and streamlining maintenance operations, while EAM provides a broader range of features that cover the entire asset lifecycle, including procurement, project management, and lifecycle cost analysis. In short, EAM offers a more comprehensive set of functions than CMMS.